Explore how Digital Sound Processors revolutionize audio in music, movies, devices, and cars, delivering crystal-clear sound like never before.
Introduction
DSP
DSP stands for Digital Signal Processing, a technology used to analyze and modify signals like audio, video, and sensor data. Digital Sound Processor improves sound quality, removes noise, and enhances system performance. It is widely used in phones, audio systems, medical devices, and communication tools.
DSPs
DSPs (Digital Signal Processors) are specialized microchips designed to handle complex signal-processing tasks quickly. They perform fast mathematical operations required for audio, video, and sensor data. DSPs power features like noise cancellation, sound enhancement, and image processing. Their speed and efficiency make them ideal for smartphones, vehicles, and professional audio systems.
DSP Meaning
DSP meaning refers to the method of processing digital signals using mathematical algorithms. It helps improve accuracy, efficiency, and clarity in various electronic devices.
Define Digital Signal Processing
Digital Signal Processing is the technique of manipulating digital signals to improve their quality or extract useful information. It involves filtering, compression, noise removal, and real-time analysis. DSP works by converting analog signals into digital data for advanced processing. It is essential in electronics, audio engineering, telecom, and medical equipment.
Evolution of Sound Processing
Before DSPs, sound manipulation was purely analog physical knobs, circuits, and amplifiers shaping the sound waves. Then came digital technology, and with it, Digital Sound Processing, which brought precision, control, and endless possibilities.
How a Digital Sound Processor Works
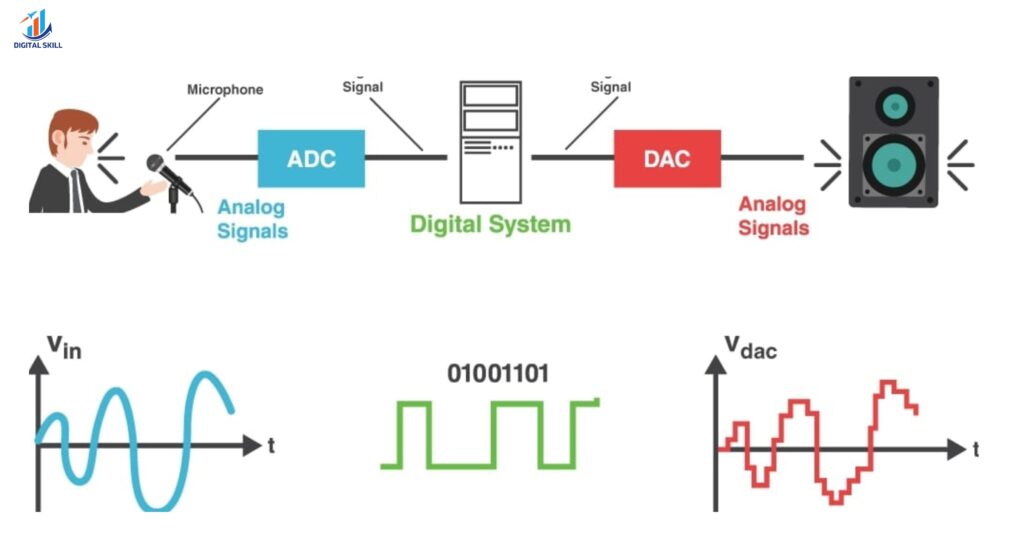
At its core, a DSP converts analog audio signals into digital data. It processes this data through algorithms that modify the sound equalizing frequencies, removing noise, or enhancing clarity before converting it back into analog form for your ears.
Types of Digital Sound Processors
Audio DSPs
Audio DSPs process digital sound to improve clarity, balance, and overall audio quality. They adjust frequencies, reduce noise, and optimize output for different devices. These processors are used in speakers, mixers, and music players. Their goal is to deliver cleaner and more accurate audio.
Automotive DSPs
Automotive DSPs enhance sound quality inside vehicles by adjusting audio according to cabin shape. They balance bass, mid, and treble for a premium listening experience. These DSPs remove road noise and improve speech clarity. Modern cars rely heavily on them for immersive audio.
Studio and Home Theater DSPs
Studio and home theater DSPs are designed for precise sound shaping and immersive effects. They support multi-channel audio, surround sound, and advanced EQ settings. In studios, they help engineers craft professional-quality mixes. In homes, they create cinema-like sonic experiences.
Hearing Aid and Mobile DSPs
Hearing aid and mobile DSPs focus on speech clarity, background noise reduction, and personalized sound. They adapt to different environments using smart algorithms. These DSPs are essential for clear calls and audio in smartphones. In hearing aids, they enhance natural listening with comfort.
Core Functions of a DSP
Equalization (EQ)
Equalization (EQ) adjusts audio frequencies to improve sound balance. It boosts or cuts specific ranges like bass, mids, or treble. EQ helps match audio to room acoustics or personal preference. It is one of the most essential tools in music and audio processing.
Compression and Limiting
Compression and limiting control volume levels to prevent distortion and maintain balance. Compression reduces dynamic range for smoother audio. Limiting sets a maximum level to avoid clipping. Together, they ensure consistent and professional sound output.
Reverb and Echo
Reverb and echo add spatial depth and natural ambiance to audio. Reverb simulates room reflections, while echo repeats sound with delay. DSPs use detailed algorithms to create realistic effects. These enhance music, vocals, and cinematic audio experiences.
Noise Reduction and Cancellation
Noise reduction and cancellation remove unwanted sounds for cleaner audio. DSPs analyze and subtract background noise using smart filtering. Active noise cancellation (ANC) improves clarity in calls and music. This function is vital in smartphones, earbuds, and recording devices.
Applications of DSP in Everyday Life
Music and Entertainment
Music and entertainment rely on DSPs for better sound quality and special effects. DSPs shape audio in music players, streaming apps, and gaming systems. They enhance bass, clarity, and surround sound. Everyday listening becomes richer and more enjoyable.
Smartphones and Earbuds
Smartphones and earbuds use DSPs for call clarity, ANC, and audio enhancement. They improve voice quality in both recordings and calls. DSPs also optimize music playback for different earbud designs. This results in high-quality sound in portable devices.
Automotive Audio Systems
Automotive audio systems use DSPs to tailor sound to the car interior. They correct speaker placement issues and reduce road noise. DSPs enable surround sound and custom EQ profiles. This transforms in-car audio into a premium experience.
Medical and Hearing Devices
Medical and hearing devices use DSPs to enhance speech and reduce interference. Hearing aids rely heavily on DSP for natural listening. DSP helps filter out background noise in hospitals and clinics. It also assists in diagnostic audio equipment.
Broadcasting and Communication
Broadcasting and communication depend on DSPs for clear transmission and stable audio. DSP improves voice quality in radio, TV, and online streams. It reduces noise, stabilizes sound, and manages bandwidth efficiently. This ensures professional audio delivery across platforms.
DSP in Professional Audio Engineering

Studio Mixing and Mastering
Studio mixing and mastering heavily use DSPs for precise sound shaping. They control EQ, compression, reverb, and stereo imaging. DSP tools ensure tracks sound balanced across all playback devices. Engineers rely on them for polished, professional results.
Live Sound Optimization
Live sound optimization uses DSPs to manage acoustics in real time. They prevent feedback, adjust EQ, and balance speaker output. DSPs adapt to venue size and audience movement. This ensures clear and powerful sound during concerts and events.
Integration with Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
Integration with DAWs allows DSP plugins and processors to enhance production quality. DSP-based tools handle heavy audio processing with accuracy. They provide effects, mixing controls, and real-time signal shaping. This integration is essential for modern music production.
The Role of DSP in Automotive Systems
- Adapt audio to cabin size and materials.
- Reduce road and engine noise.
- Improve in-car voice command systems like Siri or Alexa Auto.
DSPs make every drive sound like a concert on wheels.
DSP in Mobile and Smart Devices

DSP in mobile and smart devices processes audio in real time to deliver clear calls, crisp music, and improved voice recognition. It powers features like noise cancellation, voice assistants, and sound enhancement in apps. Modern smartphones rely on DSPs to manage speech clarity and reduce background noise. These processors make everyday communication smoother and audio experiences more immersive.
Advantages of Digital Sound Processing
- Precision:
- Customization:
- Efficiency:
- Versatility:
Limitations of DSP Technology
Latency issues
Latency issues occur when DSP processing takes extra time, causing slight delays in audio output. This can affect real-time applications like gaming, live sound, and voice communication.
Cost of implementation
Cost of implementation is higher because DSP systems require advanced processors and specialized software. This makes them more expensive compared to traditional analog solutions.
Complexity in design
Complexity in design arises due to the need for skilled engineering and detailed algorithm development. This makes DSP systems harder to build, integrate, and optimize.
Modern Innovations in DSP
The latest DSPs now integrate AI to adapt sound automatically.
Features like 3D audio, spatial sound, and adaptive noise cancellation create immersive and personalized experiences.
How to Choose the Right DSP
When selecting a DSP, consider:
- Purpose: Music production, car tuning, or home theater.
- Power: More processing power allows more complex adjustments.
- Compatibility: Ensure it integrates well with your setup.
Top brands like miniDSP, Helix, AudioControl, and JL Audio lead the market.
The Future of Digital Sound Processing
The future of DSP lies in AI-driven real-time audio adaptation. Imagine headphones that instantly adjust to your environment or cars that tune sound based on passenger location.
DSPs will continue to shape how we experience sound making it richer, smarter, and more immersive.
Conclusion
Digital Sound Processors have revolutionized how we hear and feel sound. From your favorite songs to the voice of your GPS, DSPs quietly perfect every audio experience. As technology evolves, expect DSPs to blend even more seamlessly into our lives creating soundscapes that feel alive and personalized.
FAQs
What process converts analog sound waves into digital sound?
The process is called Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC), where sound waves are sampled and converted into numeric data. This allows audio to be stored, processed, or transmitted digitally.
What is digital sound processing?
Digital sound processing is the use of algorithms to enhance, modify, or analyze audio signals. It improves clarity, reduces noise, and adds effects like EQ, compression, and reverb.
What process converts analog sound waves into digital sound?
The ADC process captures continuous sound waves and transforms them into binary data. This digital form can then be edited, filtered, or enhanced using DSP technology.
What is a DSP for car audio?
A DSP for car audio customizes sound based on vehicle acoustics, speaker placement, and listener position. It improves clarity, bass response, and overall audio quality inside the car
What does DSP stand for in audio?
In audio, DSP stands for Digital Signal Processing, the technology used to shape and improve sound. It handles EQ, crossover control, time alignment, filtering, and noise reduction.
What is the best DSP for car audio?
The best DSP for car audio depends on budget and setup, but popular choices include Helix, Audison, and JL Audio DSP units. These offer high-quality tuning, clean processing, and advanced customization options.